|
|
The features on this page require an add-on to work with GENESIS64 Basic SCADA. |
|
|
The features on this page require an add-on to work with GENESIS64 Basic SCADA. |
SNMP stands for Simple Network Management Protocol, and is a simple protocol that allows devices to expose useful information to other devices. This information can be the CPU fan speed of a computer or the routing table of the router. Almost every network device answers to SNMP requests. SNMP gives Network Managers access to information from nearly every device connected to the Network.
An SNMP network consists of a Network Management System (NMS), Managed Devices, and agents. NMS is software that collects data from the devices, organizes it, and shows it to the end user. The ICONICS SNMP connector functions as a manager in an SNMP scenario. An NMS would monitor or control managed devices that provide SNMP information through the agents. An agent is software that runs on a device (such as a router, printer or PC) and answers to the messages from the NMS. These messages can either be read messages (NMS wants to retrieve data) or write messages (the manager wants to set data). The agent can also send a trap to the NMS. A trap is a notification similar to an alarm, such as "the CPU Temperature is too high!" For more information, refer to SNMP Basic Components, and SNMP Basic Commands.
Each variable that SNMP can read/write is identified in the form of an Object Identifier (OID). The OID identifies the information in a sequence of numbers. For example, 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1 is an OID that describes the description (sysdescr) of the device. All of the OIDs for a device make up the MIB (Management Information Base), which represents all the data that the device can expose through SNMP. This information for a device is provided by the manufacturer in the form of a MIB text file. This MIB file acts as a dictionary for the device. The MIB files can be used by the NMS to translate numerical OID strings into human-readable text. For example, 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1 can be translated as "iso.org.dod.internet.mgmt.mib-2.system.sysdescr", which describes the location for sysdescr (the description of the system) that is inside the folder "system" which is inside "mib-2", and so on. This is explained in more depth in the Management Information Base (MIB) in SNMP Connector topic.
SNMP Connector available to you with GENESIS64 is a set of applications that allows you to create your own Network Management Systems. It allows you to manage the network through SNMP and perform Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA through OPC) with the very same application. Moreover, you can monitor and manage the Ethernet-based PLC-control networks through SNMP for a complete and universal network management.
Network Management Using SNMP Connector
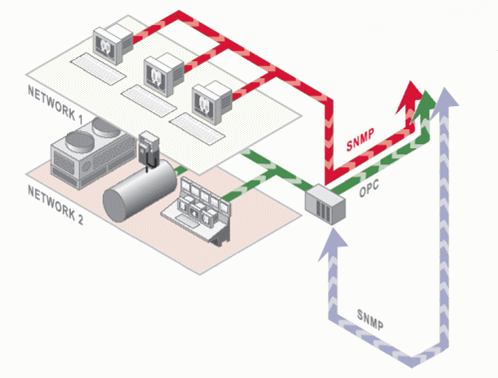
With SNMP Connector, you can quickly analyze a network, discover new devices, and create SNMP tags. However, this is just a little part of what is possible to do with SNMP Connector. Searching through the MIBs of the devices, you can find multiple types of information. Within the SNMP Connector, the only limit to what is possible to do with SNMP is just the imagination.
The SNMP Connector Suite consists of:
SNMP Explorer: Through a fast network scan, SNMP Explorer retrieves all the SNMP agents over a network and shows you all the information contained in the MIB through a simple tree structure.
SNMP Configurator: This is the core of the SNMP Connector. Here you can organize all the information retrieved through SNMP and modify the SNMP tags.
You will need to configure Windows to support SNMP. You can find more details on how to setup windows by following the application note entitled "SNMP Connector - Setting up Windows" to support SNMP Connectivity. You must also make sure SNMP is installed correctly. For help doing this, refer to Installing SNMP on the Machine. Once it is installed, you can Add the SNMP Connector to the Workbench.
Now you can create an SNMP configuration database, which is described in Configuring Databases Using SNMP Connector.
See also:
SNMP Explorer/Edit Network Settings
Creating a New MIB Folder in SNMP Connector
Importing Configuration Data to SNMP Connector