The system configuration when using Mitsubishi Electric FA Connector allows for configuring a MELSEC device within ICONICS Workbench. See MELSEC System Configuration for more info.
Note: MELSEC devices can only be edited when disabled. Device configurations are validated when activated. When the device is activated, settings can not be changed until the device is disabled. See Activate and Disable.
To Add MELSEC
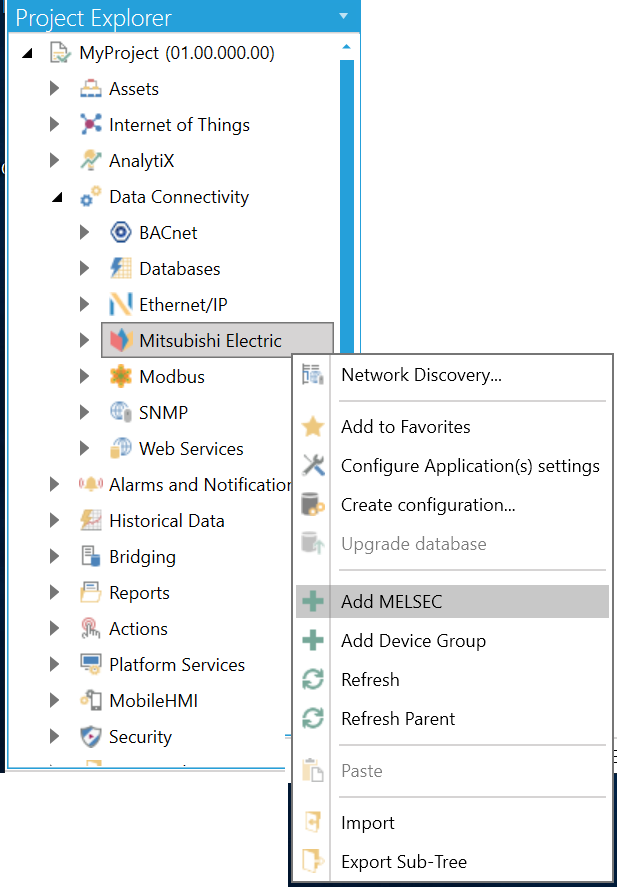
In the Workbench, expand your project in the Project Explorer, and then expand the Data Connectivity node. Right-click the Mitsubishi Electric node and click on Add MELSEC, as shown below.
Add MELSEC via the Project Explorer in the Workbench
-OR-
Select the Mitsubishi Electric node in the Project Explorer in the Workbench and then click on the Add MELSEC button, shown below, in the Edit section of the Home ribbon.
Add MELSEC Button

This opens the MELSEC Properties, shown below, in the middle section of the Workbench. Enter a name for the MELSEC device in the Name text entry field.
MELSEC Properties
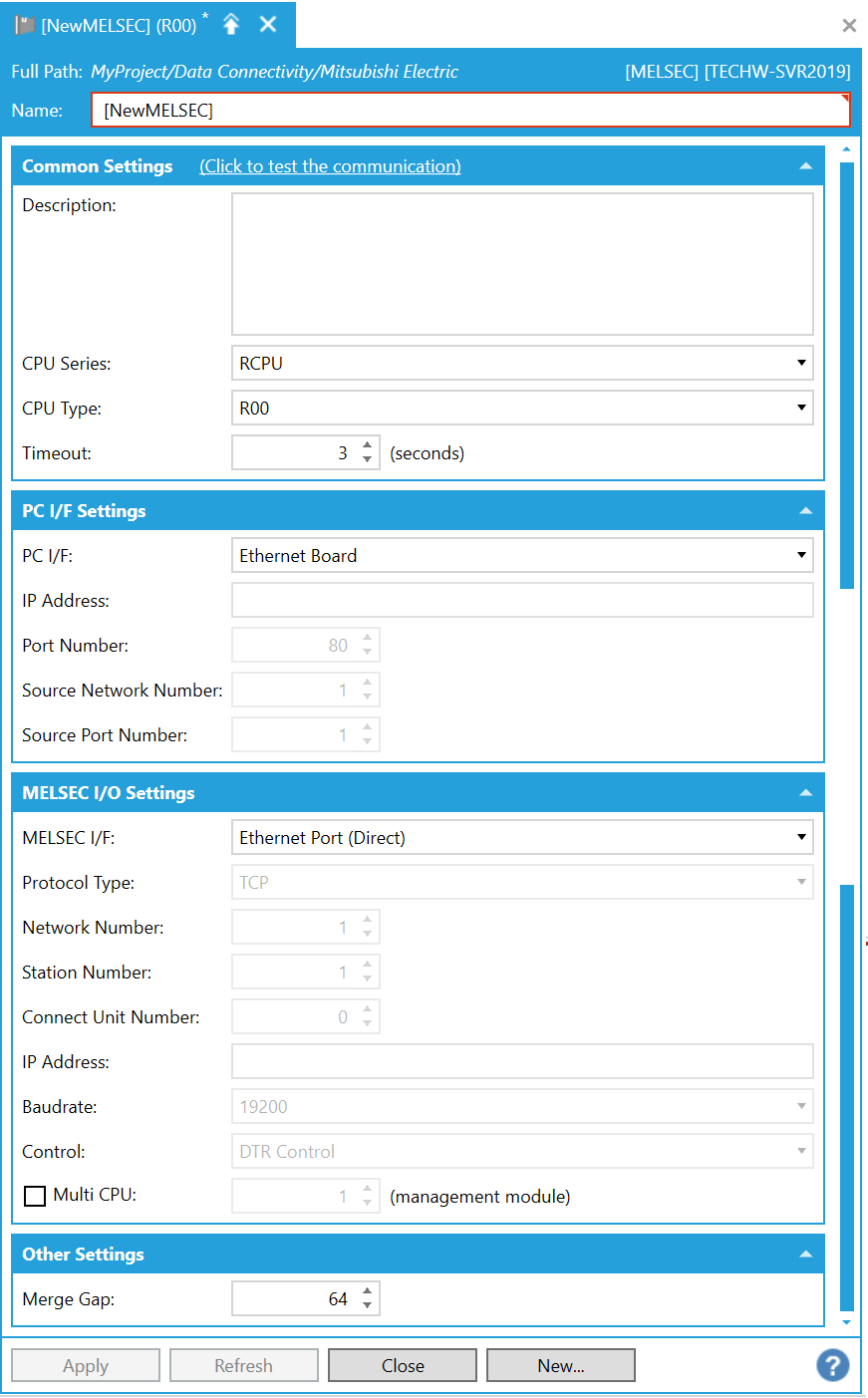
Common Settings
(Click to test the communication) - Click this link to connect to the actual device for test.
Description - Enter a description for the MELSEC device in the text entry field.
CPU Series - Use the pulldown menu to select from RCPU or FXCPU. [Note: See MELSEC System Configuration for additional compatible system-related details.]
CPU Type - Use the pulldown to select a CPU type, which is based on the selected CPU Series above. [Note: See MELSEC System Configuration for additional compatible system-related details.]
If RCPU CPU Series Selected: R00, R01, R02, R04, R08, R16, R32, R120, R04EN, R08EN, R16EN, R32EN, R120EN, R08SF, R16SF, R32SF, R120SF, R08P, R16P, R32P, R120P, R08PSF, R16PSF, R32PSF, R120PSF
If FXCPU CPU Series Selected: FX5U(FX5UC), FX5UJ
Timeout - Enter a timeout, in seconds, in the text entry field (or use the up/down arrow buttons) to cease communications attempts upon error.
Retry - Enter a number of communication retries in the text entry field (or use the up/down arrow buttons).
PC I/F Settings
PC I/F - Use the pulldown menu to select a PC I/F (interface function) from USB, Serial, Ethernet Board, or CC IE Control Board. [Note: See System Configuration for additional compatible system-related details.]
IP Address - Enter the IP address for the PC I/F (interface function) in the text entry field.
COM Port Number - Enter a COM port number for the PC I/F (interface function) in the text entry field (or use the up/down arrow buttons).
Source Network Number - Enter a source network number in the text entry field (or use the up/down arrow buttons).
Source Port Number - Enter a source port number in the text entry field (or use the up/down arrow buttons).
Board No - Use the pulldown menu to select from 1st Module to 4th Module for CC-Link IE Control Board.
MELSEC I/O Settings
MELSEC I/F - Use the pulldown menu to select a MELSEC I/F (interface function), which is based on the combination of CPU Series, CPU Type, and PC I/F settings above. Note that some of the settings in the remainder of this section may be active or inactive based on the selection of the specific CPU Series, CPU Type, and PC I/F combinations. [Note: See MELSEC System Configuration for additional compatible system-related details.]
Protocol Type - For Ethernet Board interfaces that require '(Specify IP Address)', use the pulldown menu to select from either TCP or UDP.
Network Number - For Ethernet Board interfaces [specifically RJ71EN71 (Direct), or RJ71EN71 (Specify IP Address)], or CC-Link IE Control Board interfaces, enter a network number in the text entry field (or use the up/down arrow buttons).
Station Number - For Ethernet Board interfaces [specifically RJ71EN71 (Direct), or RJ71EN71 (Specify IP Address)], or CC-Link IE Control Board interfaces or Serial interfaces, enter a station number in the text entry field (or use the up/down arrow buttons).
IP Address - For Ethernet Board interfaces that require '(Specify IP Address)', enter an IP address for the MELSEC I/F in the text entry field.
Baudrate - For Serial interfaces, use the pulldown menu to select a baudrate from 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, or 115200.
Control - For Serial interfaces, use the pulldown menu to select from DTR Control, RTS Control, DTR and RTS Control, or DTR or RTS Control.
Redundant Mode - When active, check this box if you want to access Redundant CPU. You can use the nearby pulldown menu to select from Not Specified or Control System.
Other Settings
Merge Gap - Enter a value larger than the number of registers between tags when reading inconsecutive registers in a batch in one communication between Mitsubishi Electric FA Connector and a MELSEC device. This setting is for adjustment and is usually left at its default value of 64.
Marge Gap Details
Inconsecutive registers can be read in a batch in one communication between Mitsubishi Electric FA Connector and a MELSEC device by setting a value larger than the number of registers between tags to be monitored for "Merge gap".
Reading inconsecutive registers in a batch reduces the number of times of communication, which may increase the communication speed.
If the number of registers between tags exceeds a value set for "Merge gap", inconsecutive registers are read in multiple communications.
Example:
When monitoring tags for which inconsecutive registers are set:
Registers set for a tag to be monitored: D20 to D50, D60 to D100, D200 to D300
Registers between tags to be monitored: D51 to D59 (9 points)
Registers between tags to be monitored: D101 to D199 (99 points)
When setting '9' for "Merge gap"
D20 to D100 can be read in a batch in one communication because the number of registers for �b� does not exceed a value set for "Merge gap". D60 to D100 and D200 to D300 cannot be read in a batch in one communication because the number of registers for �c� exceeds a value set for "Merge gap". Therefore, D20 to D100 are read in a batch in one communication, and D200 to D300 in a next communication.
When setting '100' for "Merge gap"
D20 to D100 can be read in a batch in one communication because the number of registers for �b� does not exceed a value set for "Merge gap". D60 to D300 can be read in a batch in one communication because the number of registers for �c� does not exceed a value set for "Merge gap". Therefore, D20 to D300 are read in a batch in one communication.
Precautions:
If setting a value larger than the number of registers between tags for "Merge gap" when the number of tags to be monitored is small, the communication speed will be decreased because registers not to be monitored are also read.
Depending on a protocol to be used, the size of registers that can be read in one communication may be small.
In this case, the communication speed is decreased because registers must be read in multiple communications.
Click Apply to save your changes to the configuration and Close to return to the Workbench.
See Also: