|
|
The features on this page require a GENESIS64 Advanced license and are not available with GENESIS64 Basic SCADA . |
|
|
The features on this page require a GENESIS64 Advanced license and are not available with GENESIS64 Basic SCADA . |
A number of GENESIS64 components are servers or services that you can control and modify from the Workbench Classic. They include:
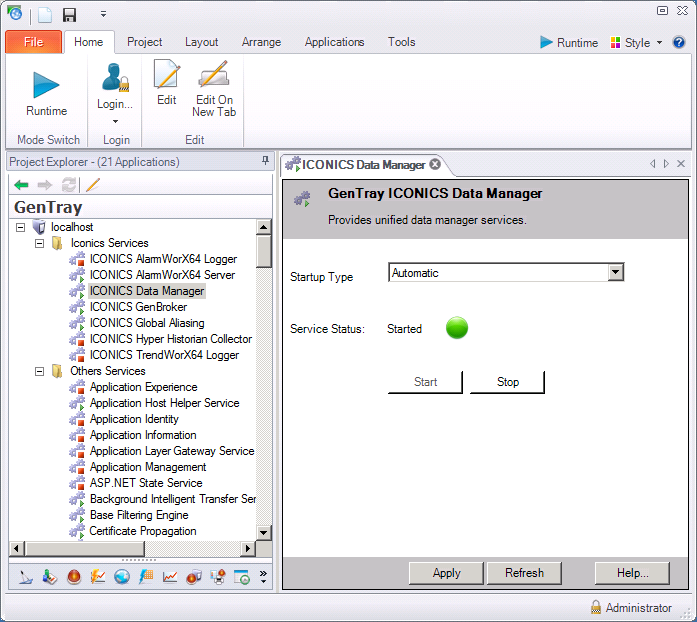
GenTray. Start and stop any service, including ICONICS and Windows services.
Use GenTray To Start and Stop ICONICS and Other Services
FrameWorX64 Server. Configure GenBroker, GenEvents, and Web services, and configure the databases that support these different methods of communications. FrameWorX64 is one of a number of GENESIS64 applications that stores its data in an XML file.
AlarmWorX64 Server. Start, stop, and configure the alarm configuration database.
TrendWorX64 Server. Start, stop, and configure the trend configuration database.
SNMP. Configure and manage the SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) service that is used to discover devices and their properties over a network.
The SNMP Network Explorer
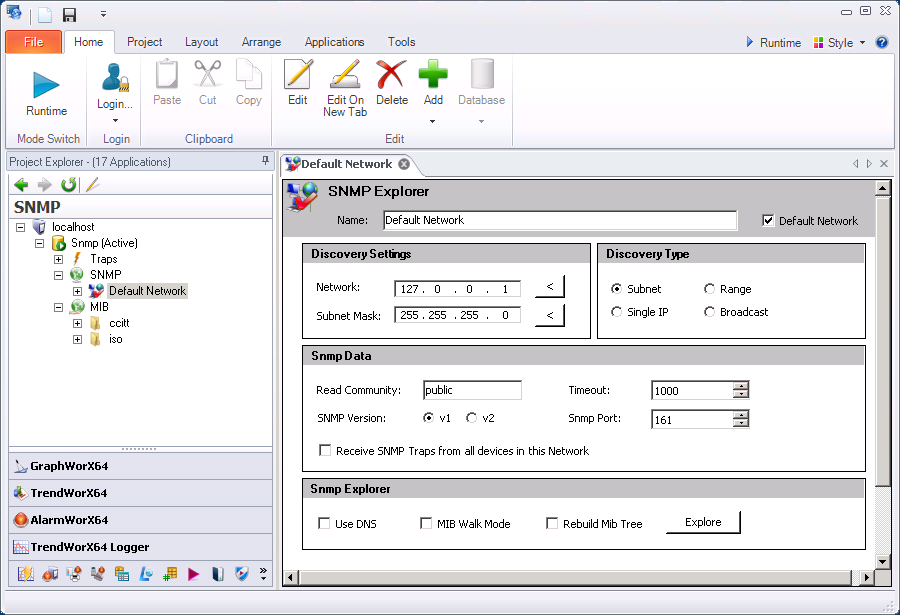
The SNMP service is an example of a server that is modified without having control over the database that stores the settings. SNMP is a network service, and although the parameters describing devices on the network called the MIB file can be edited, SNMP cannot be turned on or off for the network. However, a client can start and stop the SNMP client service locally. The Network Explorer controls some of the important aspects of the discovery process.
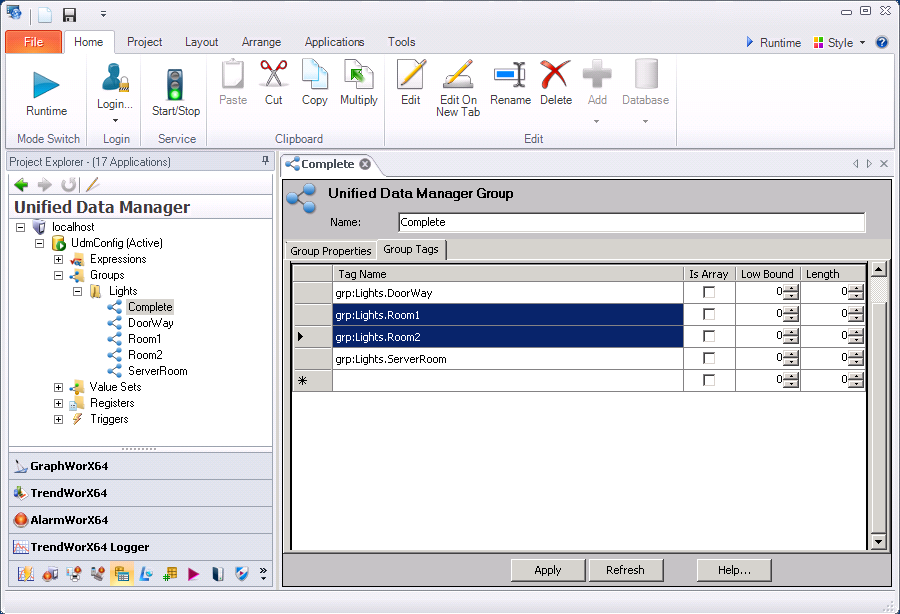
Unified Data Manager. The UDM is a central SQL database that stores expressions, subscriptions, groups, values, registers, triggers, and other data that can be used by any GENESIS64 application. The service can be started, stopped, and all of these data types and data instances can be created and modified within the UDM in the Workbench Classic .
The Unified Data Manager is a Front End to a Managed SQL Database
Security Server. The Security Server stores accounts and policies in a database organized by users and groups. You can start, stop, modify and create security policies from within the Security Server.
Global Aliasing. The Global Aliasing System (GAS) stores variable names and their values within a SQL database so that these variables can be used throughout GENESIS64 applications. Start, stop, create, and modify global aliases using this service.
Language Aliasing. The Language Aliasing System (LAS) makes substitutions for language aliases whenever the assigned language in the Language Selector dialog box is changed.
|
|
Note: Local aliasing is not a service, but local aliases can be used in GraphWorX64. They are stored within the GraphWorX64 files to which they apply. |
You can access the Workbench Classic locally, but you can also open and manage the Workbench Classic on remote systems. When managing a remote system the different objects, files, and settings are organized into different groups for each of the systems you are currently browsing.
To open and view a remote server or service:
On the Project ribbon, click the Connect to Server button in the Edit section. This opens the Connect to Server dialog box shown below.
The Connect To Server Dialog Box
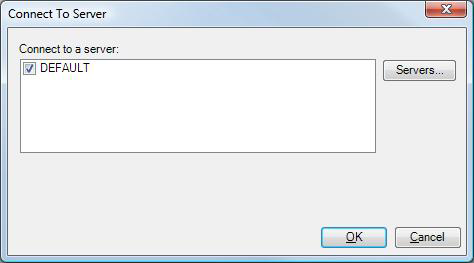
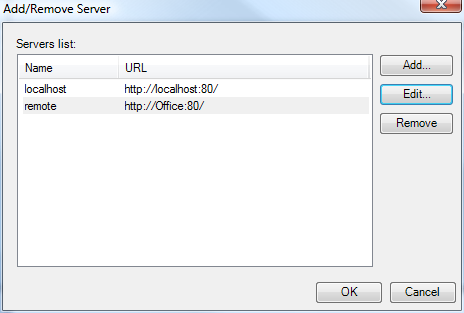
If the Remote server is not listed click the Servers button.
In the Add/Remove Server dialog box shown below click the Add button to Add a server or select the server and click the Edit button to edit the server.
The Add/Remove Server Dialog Box
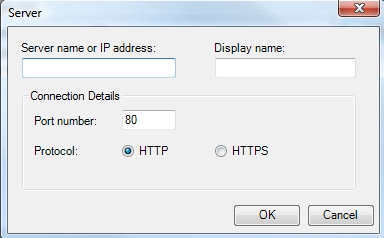
If you clicked Add, enter the Server name or IP address, Display name, and Connection Details in the Server dialog box that appears. If you clicked Edit make any changes to the fields in the Server dialog box.
Server Dialog Box
Click the OK button on all of the open dialog boxes to return to the Workbench Classic .
The Workbench Classic validates the connection to the new project server and then lists the server in the Add/Remove Project Server.
See also:
Workbench Classic User Interface