The Security Server offers nearly identical security options for user accounts and for groups. You can apply security restrictions at the group level, the user level, or both. The Security Server uses the following rules for determining whether a privilege is extended or denied to a user based on his or her security:
If a user lacks a privilege and is added to a group that has that privilege, the privilege is extended to the user.
If a user or group has a privilege that is denied, then that privilege is denied to the user even if the user was allowed that privilege at the user account level. Denials always take precedence.
Once you define a group or user account (as described in Users and Groups), you define its privileges. You do this by using the several tabs available when you define or edit the group or user.
The Application Actions section of the User or Group properties remains visible, regardless of which of the following tabs is selected.
Each tab is described below:
Many of these tabs are divided into two sections: an Include section (called Allow these operations) and an Exclude section (called Deny these operations). When you fill a line in one of these sections, click on the next blank line and enter the string. During runtime, when a GENESIS64 client sends an OPC point string, alarm, file, or other object to the Security Server for access testing (granted or denied), the include and exclude lists are string-compared as described below for each active user and group until access is granted. OPC point strings are used in this example, but the same logic applies to all objects that require access:
Compare the OPC point string with each string in the include list until a match is found. If no match is found, access is denied.
If a match is found in the include list, compare the OPC point string with every string in the exclude list. If no match is found in the exclude list, access to the point is granted, and no further testing of active groups and users is performed.
Privileges can be extended or denied to users and groups on an application-by-application basis. The Application Actions section of the User (shown below) or Group properties is where you define these privileges for a user or for a group. Each client application has its own set of actions that can be controlled, and you have precise control over each action. When you create a new user account or group, all applications and actions are selected by default. You should begin your definition of an account by visiting the Application Actions tab and setting the restrictions that you require.
Security Role Application Actions
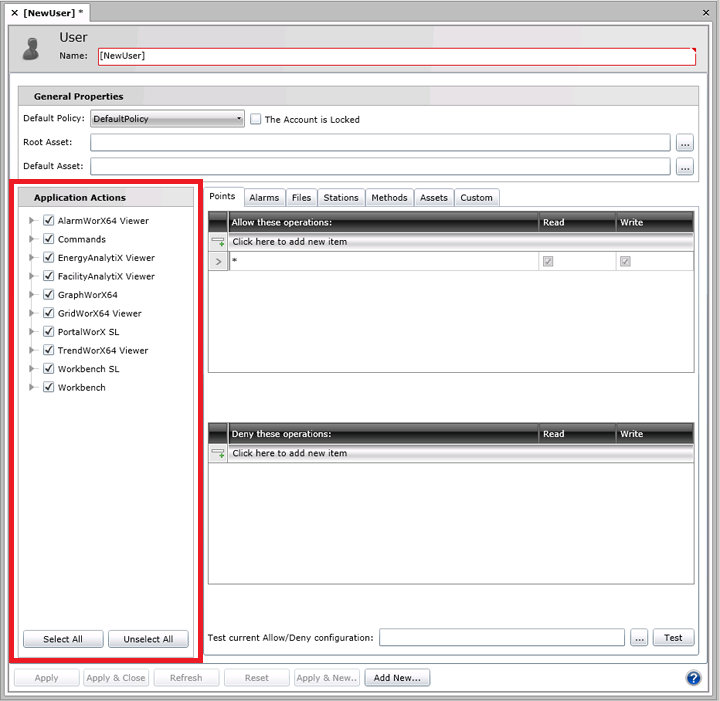
The table below lists the different applications and the actions that are available for giving access or limiting. Select the action to give users access; deselect the action to deny the ability to perform the action.
|
Application |
Actions |
Sub Actions |
|
AlarmWorX64 Viewer : |
Allow Toolbar |
|
|
Chart: |
Toggle Details Visibility |
|
|
|
Disable Notification |
|
|
|
Edit Filters |
|
|
|
Fire Custom Event |
|
|
|
Grid: |
Advanced Sorting Clean Empty Rows Column Reorder Column Resize Confirm Notification Enable Tool Tips Selection Grouping Minimize All Groups Row Resize Simple Sorting Toggle Details Visibility Toggle Group Header Visibility Unselect |
|
|
Historical Data: |
Allow Reporting Refresh Historical Data Set Historical Data Time Range |
|
|
Load and Save Configuration |
|
|
|
Real Time Data: |
Enable Acknowledge |
|
|
Runtime Filtering |
|
| Commands: | ||
|
EnergyAnalytiX Viewer: |
Configuration Mode |
|
|
Save Existing Configuration |
||
|
Save New Configuration |
||
|
FacilityAnalytiX Viewer: |
Configuration Mode |
|
|
|
Save Existing Configuration |
|
|
|
Save New Configuration |
|
|
GraphWorX64 : |
Exit Application |
|
|
|
Menu: |
Cache Display Settings Carousel Display Back-Forward Exit Runtime File Open Fit to Window Help Functions Print Functions Recent Files List Set Icon Sizes Set Language Set Main Menu Visibility Set Navigation Bar Visibility Set Scrollbar Visibility Set Status Bar Visibility Show Diagnostics Stop File Load Zoom Functions |
|
|
Mouse: |
Drag-Drop DataSource Zoom Functions |
|
|
Pick Actions: |
Close Window Compose Email Database Update Display Back Display Forward Load Display Make Phone Call Popup Menu Run Report Run Script Run Transaction Send SMS Set Global Aliases Set Language Set Local Aliases Set Object Visibility Set View Start Applications Toggle Value Write Value |
|
|
Tabs: |
Load Display |
|
GridWorX64 Viewer: |
Allow Toolbar |
|
|
Grid: |
Advanced Sorting Column Reorder Column Resize Enable Tool Tips Selection Grouping Minimize All Groups Refresh Data Row Resize Simple Sorting Toggle Column Visibility Toggle Group Header Visibility Unselect |
|
|
Load and Save Configuration |
|
|
|
Runtime Filtering |
|
|
|
TrendWorX64 : |
Allow Toolbar |
|
|
|
Comment Actions: |
Create Show |
|
|
Configuration: |
Load Save |
|
|
Cursor |
|
|
|
Data Navigation: |
Scroll Trend Set Right Time Shift Pen |
|
|
Export Data |
|
|
|
Freeze Mode: |
Enter Exit |
|
|
Historical Update Actions: |
Delete Sample Insert Sample Update Sample |
|
|
Legend: |
Show-Hide |
|
|
Pen Actions: |
Add Pen Delete Pen Edit Pen Stack-Unstack Switch Plot |
|
|
Refresh Data |
|
|
|
Side Panel: |
Show-Hide |
|
|
Trend Actions: |
Edit Period Edit Trend Show-Hide Axis Swap Axis |
|
|
Zoom |
|
|
Workbench Silverlight: |
Configuration Mode |
|
|
Exit Application |
|
|
|
Layout Management: |
Close Document Edit New Open |
|
|
Project Management: |
Edit New Open |
|
|
Runtime Mode |
|
|
|
Workbench : |
AlarmWorX64 Logger : |
Add-Remove Database Browse Items Delete Items Edit Items Start-Stop Server |
|
|
AlarmWorX64 Multimedia: |
Add-Remove Database Browse Items Delete Items Edit Items Start-Stop Server |
|
AlarmWorX64 Server : |
Add-Remove Database Browse Items Delete Items Edit Items Start-Stop Server |
|
|
|
BACnet: |
Add-Remove Database Browse Items Delete Items Edit Items Start-Stop Server |
|
|
Exit Application |
|
|
|
FrameWorX Server: |
Add-Remove Database Browse Items Delete Items Edit Items |
|
|
GenTray: |
Browse Items Edit Items Start-Stop Server |
|
|
Global Aliasing: |
Add-Remove Database Browse Items Delete Items Edit Items Reload Configuration |
|
GridWorX: |
Add-Remove Database Browse Items Delete Items Edit Items |
|
|
|
Hyper Historian : |
Add-Remove Database Browse Items Delete Items Edit Items Start-Stop Server |
|
|
Language Aliasing: |
Add-Remove Database Browse Items Delete Items Edit Items |
|
|
Layout Management: |
Arrange Documents Carousel Close Document Delete File New File Open Gallery Maximize Document |
|
|
Mode Configuration |
|
|
|
Mode Runtime |
|
|
|
Project Management: |
Delete Edit File New File Open Pack Unpack |
|
|
ScheduleWorX64 |
Add-Remove Database Browse Items Delete Items Edit Items Monitor Mode Override Start-Stop Server |
|
|
Security Server: |
Add-Remove Database Browse Items Delete Items Edit Items |
|
|
SNMP: |
Add-Remove Database Browse Items Delete Items Edit Items |
|
|
Templates: |
File New File Open Gallery Template Editor |
|
|
TrendWorX64 Logger : |
Add-Remove Database Browse Items Delete Items Edit Items Start-Stop Server |
|
|
Unified Data Manager : |
Add-Remove Database Browse Items Delete Items Edit Items Start-Stop Server |
A GENESIS64 application that is configured to send outputs to points in OPC servers will disable them if denied by the Security Server. OPC point names (with or without wild cards) are placed in include or exclude lists for each user or group.
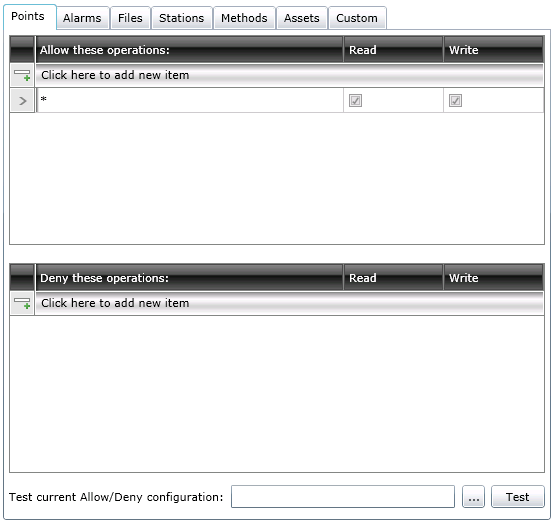
Before a GENESIS64 client outputs a process value to an OPC server, the unique string that identifies the OPC output point is sent to the Security Server to determine if the write should be allowed based on the currently logged-in users and/or the groups to which they belong. Use the Points tab of the Properties form, shown in the figure below, to configure which OPC output points are allowed to be written to by users and groups. Refer to Granting or Denying Access for a description of how entries on this tab are used. Refer to Wildcards and Performance Optimization for a description of the wild cards you can use.
Points Tab
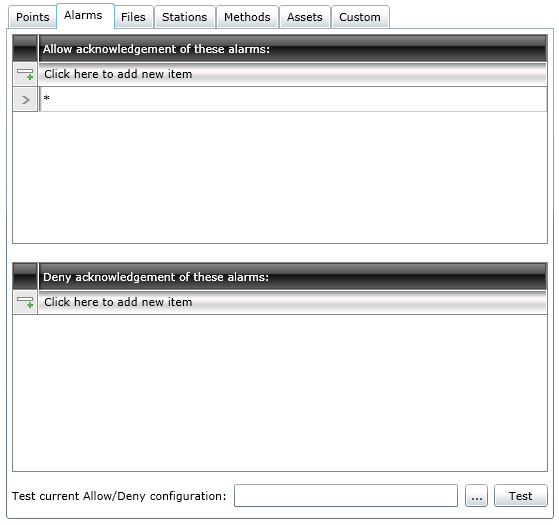
You can protect individual alarms or groups of alarms by securing those alarms. Do so by placing alarm names with or without wildcards in include (allow acknowledgement) or exclude (deny acknowledgement) lists for each user or group. (Include and exclude lists are commonly used by file backup programs to specify a backup set.) A GENESIS64 application will query the Security Server for alarm access before opening a file. Use the Alarms tab (shown below) to control access to alarm acknowledgement during runtime. Refer to Granting or Denying Access for a description of how entries on this tab are used. Refer to Wildcards and Performance Optimization for a description of the wild cards you can use.
Alarms Tab
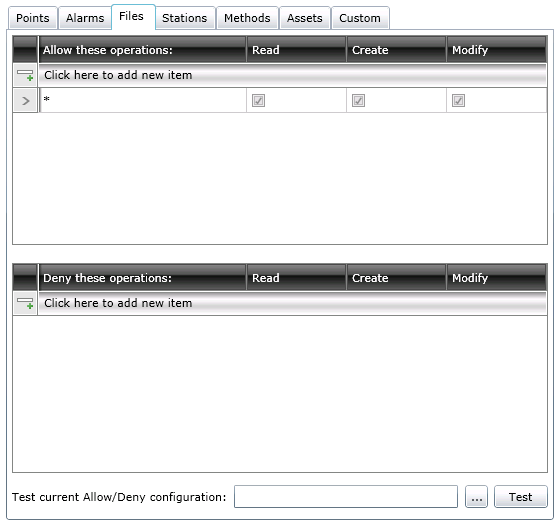
The Files form (shown below) controls access to files that GENESIS64 clients may open during runtime. You can use any of the features that are available, but all are optional and should be used only in accordance with policy strategies you have set up at your company. This tab is frequently used to define user access to GraphWorX64 display files; some users create the files and need complete access to the files they create, while others are runtime users such as dashboard operators or supervisors who much monitor operations.
In the Allow These Operations section, identify the files that the user can access then select the actions that are allowed for each file. In the Deny These Operations section, identify the files and actions that users are specifically denied. In both sections, you can use wild cards to include multiple files with one entry.
Refer to Granting or Denying Access for a description of how entries on this tab are used. Refer to Wildcards and Performance Optimization for a description of the wild cards you can use. The runtime processing and wildcard pattern matching apply here with the following differences:
The pattern matching is done on the file extension, separate from the file name, to match the DOS wildcard semantics. For example, the wildcard string to indicate all files is *.*
You must specify the file path (or include * before the filename).
Files Tab
The Stations form is used to grant (allow login) or restrict (deny login) access from specific nodes on the network. Each node on a Microsoft network is identified by a unique computer name. Refer to Granting or Denying Access for a description of how entries on this tab are used.
Stations Tab
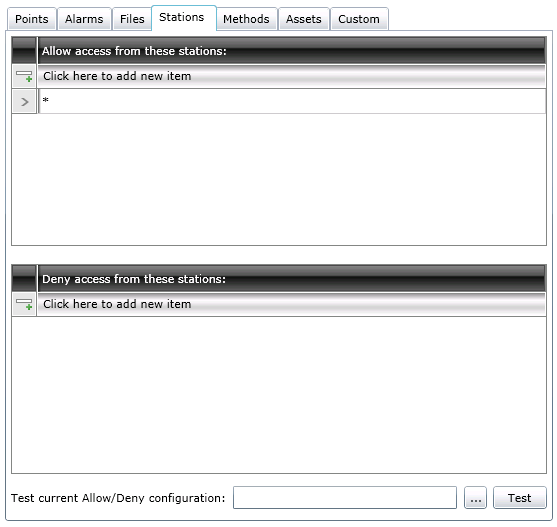
When you click the Ellipsis button [...], the Select a Station dialog box appears, as shown in the figure below. Select the Station Name from the drop-down list, or enter the name or system IP address into the drop-down list box to define the station criteria.
Select a Station Dialog Box
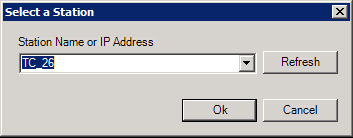
The Methods tab (shown below) is used to grant or restrict the use of listed methods.
Methods Tab
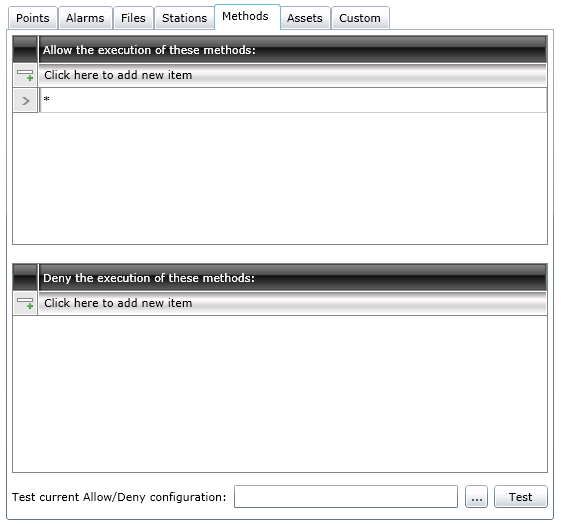
The Assets Tab (shown below) is used to grant or restrict the visualization and/or execution of listed assets in a connected asset catalog database through the AssetWorX provider in the Workbench.
Assets Tab
VBA Scripts may use custom-defined strings as security tokens that are evaluated by the Security Server. As with the file names, custom strings with or without wildcards are placed in include (allow access) or exclude (deny access) lists for each user or group. The Custom form, shown below, is used to include or exclude strings that will be tested in runtime by VBA scripts executing within GENESIS64 clients. The meaning of these strings and the functionality they protect are controlled entirely by the author of the VBA script.
Refer to Wildcards and Performance Optimization for a description of the wild cards you can use. Refer to Granting or Denying Access for a description of how entries on this tab are used. For example, from a GENESIS64 VBA script, a custom security item is tested by calling the method TestCustomSecurityItem(BSTR customString) in the GwxDisplay object.
Custom Tab
See also: