In Hyper Historian, calculated tags are calculated in accordance with their triggers on an ongoing basis. There may be a time at which you will want to recalculate the calculated tags that are already stored in Hyper Historian, for example after new historical data is added or historical data has been updated. You can recalculate calculated tags by using the Calculation Tasks Management form (shown below), available in Hyper Historian under the System Administration node. You can schedule a task to run at a specific time in the future, or you can run it immediately.
|
|
Note. Tasks are stored in a text file that you can update manually or by using an automated process; you are not required to use the Hyper Historian form provided for you in the GENESIS64 Workbench. For more information, refer to the Calculation Tasks File section at the end of this topic. |
To Set Up a Task for Recalculating Historical Calculated Tags:
Start the Workbench, then expand your project. Next, expand the Historical Data node to show the Hyper Historian node. Expand the Hyper Historian node to show the System Administration node.
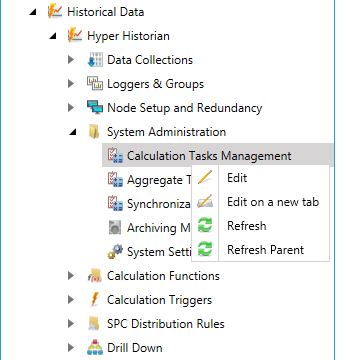
Expand the System Administration node in the navigation tree and right-click on the Calculation Tasks Management node, as shown below, then click on Edit or Edit on a new tab.
Editing Calculation Tasks Management from Project Explorer
-OR-
Select Calculations Tasks Management, then click on the Edit button, shown below, in the Edit section of the Home ribbon in the Workbench.
Edit Button

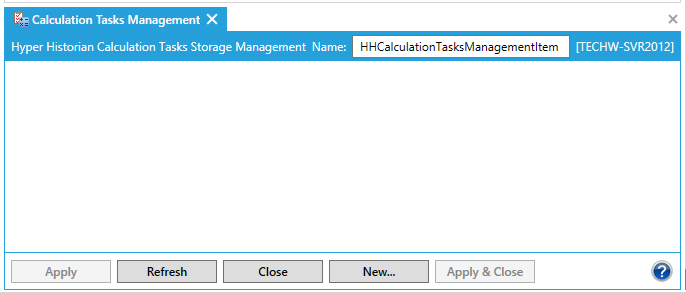
This opens the Calculation Tasks Management properties window, shown below, beneath the Project Details section in the Workbench. Enter a name in the Hyper Historian Calculation Tasks Storage Management Name text entry field.
Calculation Tasks Management Properties
To enable periodically polling the status of task processing, put a checkmark in the Enabled checkbox. This allows the Processing Task bar to show you the current status of storage processing. If the Enabled checkbox is empty, the Processing Task status does not provide a monitor for task processing.
To add a task for recalculating calculated tags, click the Add Task button [![]() ]. This opens the Add Calculation Task dialog box.
]. This opens the Add Calculation Task dialog box.
If you want timestamps to be in the client's local time, leave the check mark in the Times Are In Local Time check box. To use UTC times for the timestamps, remove the check mark from the box.
In the Execution Time box, schedule a time for the recalculation to run.
To start the recalculation now (that is, as soon as you click the Okay button), put a check mark in the Now check box.
Alternatively, to execute the task at a specific date and time, leave the Now check box unchecked and enter the Date, Hour, Minute, and Second in the Execution Time box instead.
When a task runs, a progress meter appears in the Storage Monitoring section at the top of the window, and a timer shows how long the task has been running.
The Last Modification Time field at the top of the window displays the last time the task list was changed.
Tasks are stored in a text file that you can update manually or by using an automated process. You can use this file to schedule recalculation tasks instead of Hyper Historian's Calculation Tasks Management form in the GENESIS64 Workbench.
The Calculation Tasks file's default location is:
system:\ProgramData\ICONICS\HyperHistorian\Logger\CalculationTasks
This file is a text file with an INI file like structure, in that it contains a set of keyword=Value; sections.
Valid keywords for sections in the file are:
The following is an example of recalculation task structure:
Begin=20110623T04-00-00;End=20110624T04-00-00;Exclusive=True;TagFilter="";
For additional descriptions of these values, refer to the discussions at the top of this topic.
See Also:
Synchronization Tasks Management