|
|
The features on this page require a GENESIS64 Advanced license and are not available with GENESIS64 Basic SCADA . |
|
|
The features on this page require a GENESIS64 Advanced license and are not available with GENESIS64 Basic SCADA . |
ICONICS Hyper Historian logs data to a proprietary database. While you can use the TrendWorX64 and TrendWorX32 Viewers to see and edit your logged data in a graphical format, you may wish to create reports for the logged data or edit data in bulk. For this reason, Hyper Historian comes with a SQL Provider that allows you to use common SQL Data Manipulation Language (DML) queries to retrieve and edit data.
This topic provides the following information:
Provider Capabilities and Limitations
Microsoft SQL Server Specifics
To get started, refer to the SQL Query Engine Quick Start topic.
VC Redistributable files for VS2012, ICONICS Hyper Historian, Microsoft SQL Server 2005 (or higher) and Microsoft SQL Management Studio, Microsoft Excel 2003 (or higher) installed on machine.
The HyperHistorian SQL Query Engine is developed, tested and validated against the Microsoft OLE DB RowsetViewer (version 2.70.7531.0).
Due to the provider's nature, a limited range of SQL features is supported. Catalogs, schemata and tables are predefined (by the Hyper Historian HDA Server). You can use only DML (Data Manipulation Language) queries (i.e. SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE). Also, the stored procedures are implemented in the Hyper Historian SQL Query Engine.
Individual query types have specific limitations to the query structure, as well. These limitations are detailed in an appropriate query section. In addition, advanced consumers (e.g. Microsoft SQL Server) may perform query analysis (or preprocessing) and may change the original query. This may lead to unexpected results. These rarities will be described later.
ICONICS' Hyper Historian SQL Query Engine was developed as an in-proc COM server. The whole provider is divided into several DLL libraries (modules). You can use the provider in 32-bit and 64-bit clients.
GenericOleDbProvider.dll
HHOleDbProvider.dll
HHRawDataProvider.exe
RawDataProviderPS.dll
GenericOleDbProvider64.dll
HHOleDbProvider64.dll
RawDataProviderPS64.dll
GenericOleDbProvider.dll, GenericOleDbProvider64.dll -- This module communicates with a SQL client. The module processes data from the HHRawDataProvider.exe and provides it in the form of tables and stored procedures to the client.
HHOleDbProvider.dll, HHOleDbProvider64.dll -- This is the main module of the provider. The module performs registration of the OLE DB Provider.
HHRawDataProvider.exe -- This is the module which communicates with the Hyper Historian HDA Server. The module communicates indirectly through the IcoFwxUaClient.dll library (OPC UA communication).
RawDataProviderPS.dll, RawDataProviderPS64.dll -- These files are only the proxy/stub for the HHRawDataProvider.exe module.
The QUERYSETTINGS table contains information which is used during the SQL query calculation. The table has the following structure:
|
Column Name |
Data Type |
Description |
|
TIMESTAMP_START |
DBTIMESTAMP |
Start of the timestamp range (default value – can be overloaded in the query). |
|
TIMESTAMP_END |
DBTIMESTAMP |
End of the timestamp range (default value – can be overloaded in the query). |
|
USE_USER_TIME_RANGE |
BOOL |
If the flag is set to TRUE, then the TIMESTAMP_START and TIMESTAMP_END timestamps are used for the queries. Otherwise, default timestamps (which are generated by the provider) are used for the queries. |
|
MAX_ROWS_TO_RETURN |
UI4 |
Number of rows which can be returned to the client. |
|
TREAT_UNCERTAIN_AS_GOOD |
BOOL |
For the HDA calculations. |
|
PERCENT_DATA_BAD |
BYTE |
For the HDA calculations.
|
|
PERCENT_DATA_GOOD |
BYTE |
For the HDA calculations. |
|
ALLOW_EMPTY_TAG |
BOOL |
If this value is set to true, you can run queries against the RawData table without the defining the tagname in the WHERE clause. Otherwise, these queries fail. |
The TAGS table contains information about tags, annotations and aggregates and presents list of all tags, annotations and aggregates that are available in the Hyper Historian HDA Server. The table has the following structure:
|
Column Name |
Data Type |
Description |
|
TAGNAME |
WSTR | BYREF |
Name of the tag. |
|
DESCRIPTION |
WSTR | BYREF |
Tag description. |
|
DATATYPE |
UI2 |
Information about tag’s data type. |
|
STEPPEDINTERPOLATION |
BOOL |
Stepped interpolation info. |
|
ACCESSRIGHTS |
UI2 |
Information about access rights. |
The RAWDATA table contains information about all raw data which are in the Hyper Historian HDA Server. The table has following structure:
|
Column Name |
Data Type |
Description |
|
TAGNAME |
WSTR | BYREF |
Name of the tag. |
|
TIMESTAMP |
DBTIMESTAMP |
Timestamp where the value was caught. |
|
QUALITY |
UI4 |
Quality of the value. |
|
VALUE |
VARIANT |
Value itself. |
Since Hyper Historian V10.71, we've introduced new RAWDATA tables that expose the VALUE column in a specific data type (e.g. single or string). The tables are:
|
Table Name |
VALUE Column Exposed as Data Type |
|
RAWDATA |
VARIANT |
|
RAWDATA_BOOLEAN |
BOOL |
|
RAWDATA_SINGLE |
R4 |
|
RAWDATA_DOUBLE |
R8 |
|
RAWDATA_INT8 |
I1 |
|
RAWDATA_INT16 |
I2 |
|
RAWDATA_INT32 |
I4 |
|
RAWDATA_INT64 |
I8 |
|
RAWDATA_UINT8 |
UI1 |
|
RAWDATA_UINT16 |
UI2 |
|
RAWDATA_UINT32 |
UI4 |
|
RAWDATA_UINT64 |
UI8 |
|
RAWDATA_STRING |
WSTR | BYREF |
The following SELECT syntax is supported:
SELECT [lead count restriction] expression FROM table | stored procedure [WHERE condition];
The following rules apply to individual SELECT elements:
Expression – Defines column(s) to be retrieved by the SELECT query. These may include SQL aggregate column(s) as well. But it is not possible to combine ordinal and aggregate columns together in one SQL query (we do not support GROUP BY).
Table | stored procedure – Defines table or stored procedure to select data from. It is not possible to combine table with stored procedure in one SQL query.
WHERE condition – Defines logical expression that needs to evaluate to true in order to return given table row. The expression only allows AND/OR chaining, usage of brackets, and logical comparison operators (<=, <, >, =>, <>, =).
Count restriction – Can be used to restrict number of retrieved rows. Lead restriction has form TOP x where x is number of rows to return. Note that count restrictions are applied after the query is evaluated, thus they unfortunately won’t affect performance in positive.
Be careful when you are running queries against the RAWDATA table. If the ALLOW_EMPTY_TAG in the QUERYSETTINGS table is set to ''true'', you may see the following. You can run query without the WHERE clause, but if you do so, the OLE DB Provider will get all data for all tags in the specified catalog (Logging group) and schema (Collector group). Then, the provider must sort data from all tags to one stream and this data will be sent to the output. This can take a very long time, depending on the tag count. You can set ALLOW_EMPTY_TAG to ''false''. In this case, the queries without TAGNAME in the WHERE clause will fail (such queries are not permitted).
The following INSERT syntax is supported:
INSERT INTO table (TAGNAME, TIMESTAMP, VALUE) VALUES (<tagname>, <timestamp>, <value>);
The INSERT query is supported only for the RAWDATA table. When you want to insert a new value, you have to specify TAGNAME, TIMESTAMP and VALUE. QUALITY is set automatically to ''good''. When you are using the SQL Server, use OPENQUERY for the INSERT.
Example:
INSERT INTO Signals.RAWDATA (TAGNAME, TIMESTAMP, VALUE) VALUES ('Sine', '2014-01-01 10:00:00', 25);
The following UPDATE syntax is supported:
UPDATE table SET column_name_1 = column_value_1 [, column_name_2 = column_value_2, …] [WHERE condition];
The UPDATE query can be used only against the QUERYSETTINGS and RAWDATA table. When you are updating QUERYSETTINGS table there is no WHERE clause needed. When you are updating RAWDATA table you have to specify TAGNAME and TIMESTAMP. You can update only the VALUE. QUALITY is automatically set to good. When you are using the SQL Server, use OPENQUERY for the UPDATE.
Example for the QUERYSETTINGS table:
UPDATE QUERYSETTINGS SET MAX_ROWS_TO_RETURN = 1000';
Example for the RAWDATA table:
UPDATE Signals.RAWDATA SET VALUE = 25 WHERE TAGNAME = 'Sine' AND TIMESTAMP = '2014-01-01 10:00:00';
At this time, the DELETE query is not supported by the Hyper Historian SQL Query Engine.
The following standard SQL aggregates are supported in SELECT column definition expression:
MIN
MAX
AVG
SUM
COUNT
All of these functions require column names as parameters, e.g. SELECT SUM(VALUE) FROM … . When you are using SQL aggregates, it is not possible to get other common columns. The GROUP BY clause is not supported.
The following are SQL functions:
QualityToStr
This function can be used instead of the QUALITY column. The function converts quality from DWORD representation (number) to the string, e.g. SELECT TAGNAME, QualityToStr(QUALITY) FROM RAWDATA … .
Output can be one of the following values:
Good
Bad
Uncertain
QualityToStr2
This function can be used instead of the QUALITY column. The function converts quality from DWORD representation (number) to the string, e.g. SELECT TAGNAME, QualityToStr2(QUALITY) FROM RAWDATA … .
The difference between the QualityToStr and QualityToStr2 functions is that the QualityToStr2 function returns the exact string which corresponds to the number. E.g. 10813440 means GoodNoData or 2157838336 means BadDataUnavailable.
DataTypeToStr
This function can be used instead of the DATATYPE column. Function converts data type from the WORD representation (number) to the string, e.g. SELECT TAGNAME, DataTypeToStr(DATATYPE) FROM TAGS … .
Output can be one of the following values:
VT_BOOL
VT_UI1
VT_UI2
VT_UI4
VT_UI8
VT_I1
VT_I2
VT_I4
VT_I8
VT_R4
VT_R8
AccessRightsToStr
This function can be used instead of the ACCESSRIGHTS column. Function converts access rights from WORD representation (number) to the string, e.g. SELECT TAGNAME, AccessRightsToStr(ACCESSRIGHTS) FROM TAGS … .
Output can be one of the following values:
TAG_ACCESS_RIGHTS_NONE
TAG_ACCESS_RIGHTS_READ
TAG_ACCESS_RIGHTS_WRITE
TAG_ACCESS_RIGHTS_READ_WRITE
IsGood, IsBad and IsUncertain
These functions can be used in WHERE clause. The IsGood() function selects only raw data where quality is good, likewise other functions, e.g. SELECT * FROM RAWDATA WHERE IsBad(QUALITY) = 1;
BitMask
Function provides bit mask operations. Supported operators are &, | and ^. Function can be used in WHERE clause, e.g. SELECT * FROM Signals.RAWDATA WHERE TAGNAME = 'Sine' and BitMask('&', 3221225472, QUALITY) = 0;
Date/Time functions
DateAdd, Now, NowUTC
In the WHERE clause, you can use date / time functions. You can use the DateAdd() function and you can use also Now() and NowUTC() variables, e.g. SELECT * FROM RAWDATA WHERE TIMESTAMP >= DateAdd(hh, -2, NowUTC()) and TIMESTAMP <= NowUTC(); This query returns all raw data which are 2 hours old at maximum.
Function syntax is DateAdd(DATE_PART, VALUE, BASE_TIMESTAMP), where the parameters can have the following values:
· DATE_PART
o ms – milliseconds,
o ss – seconds,
o mi – minutes,
o hh – hours,
o dd – days,
o wk – weeks,
o mm – months,
o yy – year.
· VALUE – value can be any integer.
· BASE_TIMESTAMP
o Now() – current local time,
o NowUTC() – current UTC time,
o or you can type your own timestamp in following format 'yyyy-mm-dd hh:mi:ss'.
LocalTimeToUTC
This function converts a local timestamp to the UTC timestamp. The function can be used in WHERE clause, e.g. SELECT * FROM Signals.RAWDATA WHERE TIMESTAMP >= LocalTimeToUTC('2014-01-01 10:00:00') and TIMESTAMP <= LocalTimeToUTC('2014-01-01 11:00:00');
UTCToLocalTime
This function converts an UTC timestamp to the local timestamp. The function can be used in SELECT clause, e.g. SELECT *, UTCToLocalTime(TIMESTAMP) FROM Signals.RAWDATA WHERE TAGNAME = 'Sine';
SQL stored procedures
All historical data aggregates calculations are provided through the stored procedures. In addition, more complex operations above raw data are also provided through the stored procedures as well.
The following is a list of all stored procedures supported at this time:
HDA_BOOL – calculates Duration in State 0, Duration in State 1, Number of Transitions and Count aggregates for one tag.
HDA_BOOL_5 – same functionality like HDA_BOOL but up to five tags.
HDA_ANALOG – calculates Min, Max, Average, Time Average, Totalize Average, Interpolative, Last, Delta, Range, Total and Count aggregates for one tag.
HDA_ANALOG_5 – same functionality like HDA_ANALOG but up to five tags.
HDA_REDUCED_ANALOG – calculates Min, Max, Time Average and Count aggregates for one tag.
HDA_REDUCED_ANALOG_5 – same functionality like HDA_REDUCED_ANALOG but up to five tags.
SP_RAW_DATA – gets raw data for one tag.
GET_MOST_RECENT_VALUE – returns most recent value, timestamp and quality for the specified tag name.
GET_GOOD_VALUES – returns specified count of values (first N values) with good qualities in the specified time range.
GET_BAD_VALUES – returns specified count of values (first N values) with bad qualities in the specified time range.
GET_VALUES – returns specified count of values (first N values) with good and/or bad qualities in the specified time range.
HDA_QUALITY – calculates DurationGood, DurationBad, PercentGood, PercentBad and WorstQuality aggregates
HDA_QUALITY_5 – same functionality like HDA_QUALITY but for five tags.
RAWDATA_INSERT – inserts new data into the RAWDATA table.
RAWDATA_UPDATE – updates existing data in the RAWDATA table.
GET_FILTERED_TAG_STATISTICS – calculates processed values for filtered data variables.
HDA_BOOL, HDA_ANALOG, HDA_REDUCED_ANALOG
The following is a list of input parameters for these functions:
Start timestamp – start of the timestamp range,
End timestamp – end of the timestamp range,
Resampling period – time interval size,
Tag name – when you specify only tag name (without catalog and schema) then the catalog and schema for the tag is taken from the stored procedure specification.
HDA_BOOL_5, HDA_ANALOG_5, HDA_REDUCED_ANALOG_5
The following is a list of input parameters for these functions:
Start timestamp – start of the timestamp range
End timestamp – end of the timestamp range
Resampling period – time interval size
Tag name 1
Tag name 2
Tag name 3
Tag name 4
Tag name 5
|
|
Note: When you specify only the tag name (without catalog and schema), then the catalog and schema for the tag is taken from the stored procedure specification. |
SP_RAWDATA
The following is a list of input parameters for this function:
Start timestamp – start of the timestamp range,
End timestamp – end of the timestamp range,
Tag name – when you specify only tag name (without catalog and schema) then the catalog and schema for the tag is taken from the stored procedure specification.
GET_MOST_RECENT_VALUE
The following is a list of input parameters for this stored procedure:
Tag name.
GET_GOOD_VALUES, GET_BAD_VALUES, GET_VALUES
The following is a list of input parameters for these stored procedures:
Start timestamp.
End timestamp.
Count.
Tag name.
RAWDATA_INSERT, RAWDATA_UPDATE
The following is a list of input parameters for this function:
· Tag name,
· Timestamp,
· Value,
· Quality.
GET_FILTERED_TAG_STATISTICS
The following is a list of input parameters for this function:
· Path filter – a string set of path names separated by slash character (/), names can be either fully qualified or can use wildcard characters as folder filter, path can be relative to hosting calculation,
· Name filter – a string, data variable name filter,
· Variable types – a string, where each character specifies single data variable type, when empty then it specifies all variable types (collected, calculated and aggregated), valid characters are: A … aggregated variables, R … collected (raw) variables, C … calculated variables,
· Start timestamp,
· End timestamp,
· Maximum point names to return – specifies the maximum count of variables to process in a single call (communication parameter).
EXEC GET_FILTERED_TAG_STATISTICS 'Signals*', '*Slow', 'R', DateAdd(hh, -1, NowUTC()), NowUTC(), 10;
|
Aggregate Name |
Behavior Description |
|
Min |
Retrieve the minimum value in the re-sample interval. |
|
Max |
Retrieve the maximum value in the re-sample interval. |
|
Average |
Retrieve the average data over the re-sample interval. |
|
Time average |
Retrieve the time weighted average data over the re-sample interval. |
|
Totalize average |
Retrieve the totalized value (time integral) of the data over the re-sample interval. |
|
Interpolative |
|
|
Last |
Retrieve the value at the end of the re-sample interval. The timestamp is the timestamp of the end of the interval. |
|
Duration in state 0 |
Retrieve the duration of time in the interval during which the data is equal to 0. |
|
Duration in state 1 |
Retrieve the duration of time in the interval during which the data is equal to 1 |
|
Number of transitions |
Retrieve the number of state changes a Boolean value experienced in the interval. |
|
Delta |
Retrieve the difference between the first and last value in the re-sample interval. |
|
Range |
Retrieve the difference between the minimum and maximum value over the re-sample interval. |
|
Total |
Retrieve the sum of the data over the re-sample interval. |
|
Count |
Retrieve the number of raw values over the re-sample interval. |
|
Duration good |
Retrieve the duration of time in the interval during which the data is good. |
|
Duration bad |
Retrieve the duration of time in the interval during which the data is bad. |
|
Percent good |
Retrieve the percent of data (0 to 100) in the interval which has good StatusCode. |
|
Percent bad |
Retrieve the percent of data (0 to 100) in the interval which has bad StatusCode. |
|
Worst quality |
Retrieve the worst StatusCode of data in the interval. |
For aggregate values, the status code for each returned aggregate is ''good'' if the status code for all values used in the aggregate was good.
If the status code of any value used in computing the aggregate was not good, then the server uses the TreatUncertainAsBad, PercentDataBad and PercentDataGood parameter settings to determine the status code of the resulting aggregate for the interval. Some aggregates may explicitly define their own method of determining quality.
If the percentage of good values in an interval is greater than or equal to the PercentDataGood, the aggregate is considered ''good'', otherwise it is ''bad''.
Because a value can be either good or bad only (uncertain is defined as good or bad as per ''treat uncertain as bad'' setting), percentage good = 100 – percentage bad. If a percentage good(X) is in the following range percentage bad < X < percentage good, the quality of the aggregate is Uncertain_DataSubNormal.
ICONICS Hyper Historian SQL Query Engine overrides some default pages in the Data Link Properties dialog. This is due to the fact that we don’t need all options from the default pages and, in addition, we need some special options.
The first page is a default Provider tab. You can choose any provider from the list. Our provider is called ICONICS Hyper Historian SQL Query Engine. When you double-click the Next button; the Connection tab appears.
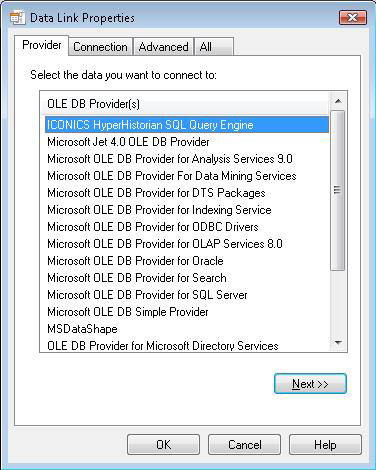
The Connection tab (shown below) is an overridden tab and allows you to set the data source, initial catalog, and schema.
Specify the location of the Hyper Historian HDA Server. If this value is not specified, the localhost is used.
Next, you can specify an initial catalog (Logging group). This catalog is used as the default catalog when the SQL queries are executed. If the initial catalog is not specified, then the default catalog is the first catalog from the list. This list is gained from the Hyper Historian HDA Server.
You can also specify initial schema (Collector group). The rules are the same as for the initial catalog. A specified schema is used as the default schema when the SQL queries are executed and so on.
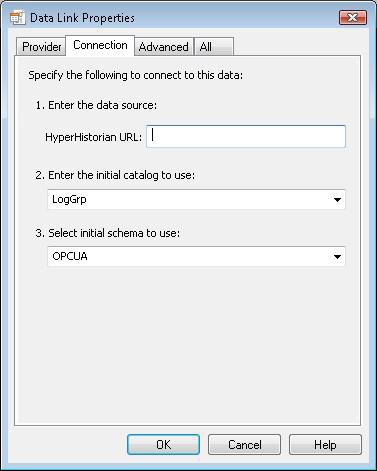
The third tab is the overridden Advanced tab, shown below. On this tab, you can specify default starting and ending timestamps. If the timestamps are specified, then the timestamps are used as default timestamps when the SQL queries are executed. These settings are applied when you run SQL queries against the RAWDATA table. When you specify timestamps in the SQL query in the WHERE clause, you will override the default timestamps.
When you don’t specify timestamps, then the default timestamps are generated every time when the query is started against the Hyper Historian SQL Query Engine. In this case, default timestamps are set subsequently. The ending timestamp is set to the current time. The starting timestamp is set to the current time minus three days (example: 2009-12-01 10:00:00, 2009-12-04 10:00:00).
Microsoft SQL Server performs specific modifications to the queries passed to the linked server (e.g., aliasing). It also performs many auxiliary operations such as data type conversions and local functions.
Microsoft SQL Server preprocessing puts limitations on the query parameters. Namely, the Microsoft SQL Server won’t propagate time specified as absolute date, e.g. '2009-01-01 12:00:00', to the provider. Instead, you must:
use date manipulation functions, i.e. dateadd(), getutcdate(), or
“hack” the conversion using nested SELECT statement, e.g. select convert(datetime, '2009-01-01 12:00:00'), or
use the OPENQUERY statement, e.g. SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY(HH2, '<SQL query>'). This solution is recommended to use in the SQL Server. Otherwise, you can fall into trouble.
When Microsoft SQL Server decides not to send the entire query to the provider, the query can be still executed and can succeed. But rather than being processed by the provider it will be processed by Microsoft SQL Server.
The problems with this approach are:
Performance – If a query, e.g. SELECT * FROM HH2.<catalog>.<schema>.RAWDATA WHERE TIMESTAMP >= '2009-01-01 12:00:00' AND TAGNAME = 'Sine'; is used, Micorosft SQL Server will execute SELECT * FROM HH2.<catalog>.<schema>.RAWDATA; against the provider. The provider won’t get information about the tag for which you can read the data. In this case, the provider will get all data for all tags in the specified catalog and schema (this may take a very long time) and after this, the Microsoft SQL Server will do the final filtering. If you want to forbid this, set the ALLOW_EMPTY_TAG in the QUERYSETTINGS to false. Then, queries like this will not be started.
Runtime limitations – Certain queries are prohibited, e.g. queries without certain limit parameters. Microsoft SQL Server might inadvertently use these queries when executing subset of user-supplied query which would lead to query execution failure.
Start Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio.
Go to the Server Objects -> Linked Servers.
You should see linked server named HH2.
Open window for new query.
Run following query: EXEC sp_catalogs HH2;.
If the provider is installed, you should get a list of all catalogs (HyperHistorian logging groups).
Run the dcomcnfg application.
Select Component Services > Computers > My Computer > DCOM Config.
In the application list, find the ICONICS Hyper Historian Raw Data Provider.
Open its properties and go to the Security tab.
Check if there is a user under which the SQL Server is running (usually NETWORK SERVICE). This user must exist in the Launch and Activation Permissions. Also, this user must exist in the Access Permissions.
If the user exists in both cases, check if there is ''all allowed'' for this user.
Confirm all changes.
Open Windows Task Manager and go to the Processes tab.
Find the HHRawDataProvider.exe process and end the process (or you can restart the computer. This should be better).
If you still can’t get any data, check if the Hyper Historian HDA Server is running properly.
Selecting all tags:
SELECT * FROM Signals.TAGS;
Selecting tag with specified name:
SELECT * FROM Signals.TAGS WHERE TAGNAME = 'Sine';
Selecting all tags (only some columns):
SELECT TAGNAME, DATATYPE FROM Signals.TAGS;
Selecting from the query settings table:
SELECT * FROM QUERYSETTINGS;
Updating information in the query settings table:
UPDATE QUERYSETTINGS SET MAX_ROWS_TO_RETURN = 1000, ALLOW_EMPTY_TAG = 0;
Selecting raw data (all tags, with default TIMESTAMPs):
SELECT * FROM Signals.RAWDATA;
Selecting raw data with specified TAGNAME and TIMESTAMPs:
SELECT * FROM Signals.RAWDATA WHERE TAGNAME = 'Sine' AND TIMESTAMP >= '2014-01-01 10:00:00' AND TIMESTAMP <= '2014-01-01 12:00:00;
[For multiple selection]
One folder:
SELECT * FROM Folder1.Rawdata WHERE Tagname = "Tag"
Two folders:
SELECT * FROM Folder1.Folder2.Rawdata WHERE Tagname = "Tag"
Three folders:
SELECT * FROM Folder1.Folder2.Rawdata WHERE Tagname = "Folder3/Tag"
Four, etc. folders:
SELECT * FROM Folder1.Folder2.Rawdata WHERE Tagname = "Folder3/Folder4/Tag"
Selecting annotations:
SELECT * FROM Signals.RAWDATA WHERE TAGNAME = 'Sine:.Annotation' AND TIMESTAMP >= DateAdd(hh, -5, NowUTC()) AND TIMESTAMP <= NowUTC();
Selecting raw data using DateAdd() function:
SELECT * FROM Signals.RAWDATA WHERE TAGNAME = 'Sine' AND TIMESTAMP >= DateAdd(hh, -5, NowUTC()) AND TIMESTAMP <= NowUTC();
Selecting raw data using QualityToStr() function:
SELECT TAGNAME, TIMESTAMP, QualityToStr(QUALITY), VALUE FROM Signals.RAWDATA WHERE TAGNAME = 'Sine' AND TIMESTAMP >= DateAdd(hh, -5, NowUTC()) AND TIMESTAMP <= NowUTC();
Selecting raw data using IsGood() function:
SELECT * FROM Signals.RAWDATA WHERE TAGNAME = 'Sine' AND TIMESTAMP >= DateAdd(hh, -5, NowUTC()) AND TIMESTAMP <= NowUTC() AND IsGood(QUALITY) = 1;
Selecting MAX, MIN and AVG value:
SELECT MIN(VALUE) AS min_value, MAX(VALUE) AS max_value, AVG(VALUE) AS avg_value FROM Signals.RAWDATA WHERE TAGNAME = 'Sine' AND TIMESTAMP >= '2014-01-01 10:00:00' AND TIMESTAMP <= '2014-01-01 12:00:00';
Running HDA_BOOL stored procedure:
EXEC Signals.HDA_BOOL '2014-01-01 10:00:00', '2014-01-01 12:00:00', 300000, 'Sine';
Running HDA_ANALOG stored procedure in SELECT query:
SELECT * FROM Signals.HDA_ANALOG('2014-01-01 10:00:00', '2014-01-01 12:00:00', 300000, 'Sine');
Examples for the SQL Server
Select rows from the RAWDATA table
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY(HH2, 'SELECT * FROM Signals.RAWDATA WHERE TAGNAME = ''Sine'';');
Running stored procedure
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY(HH2, 'EXEC Signals.HDA_BOOL ''2014-01-01 10:00:00'', ''2014-01-01 12:00:00'', 300000, ''Sine'';');
[1] – OPC Unified Architecture Specification; Part 13: Aggregates; Release Candidate; version 1.00; July 15, 2008